
Vertical velocity component Vy V x sin () 3. Horizontal velocity component Vx V x cos () 2.
For example, quadratic equations can be used to determine the height of a projectile at time 't' after the projectile has been released.The results of this lab concur with my theory, and demonstrate that one can virtually predict the range of a projectile by using the right procedures. Maximum height hmax Vy / (2 x g) Launching an object from an elevated position (initial height h > 0) 1. Although quadratic equations are often used to find maximums and minimums for problems involving projectile motion, they can also be used to evaluate the path of a projectile at various time periods. As a result, projectile motion is two-dimensional. There was the possible chance of air movement due to the air conditioning/heating system and people moving about the room, however this air movement is so picayune that error caused to the lab from this factor would be too minuscule to show up in my data. The object, in this case, travels vertically and horizontally at the same time. We performed this lab in an indoor environment that had no influence from outside factors. Moreover, human error in determining the last decimal place of the measured range values and the measured Δy value, as well as the placement of the range target paper at the predicted range measurement could affect the resulting average range. I do not think wind resistance is a factor in this lab.

When aligning the mini launcher at 40.0° and the tape measure from the ground to the mini launcher using a plumb bob, parallax error could affect the resulting measurements due to the angle of observation.
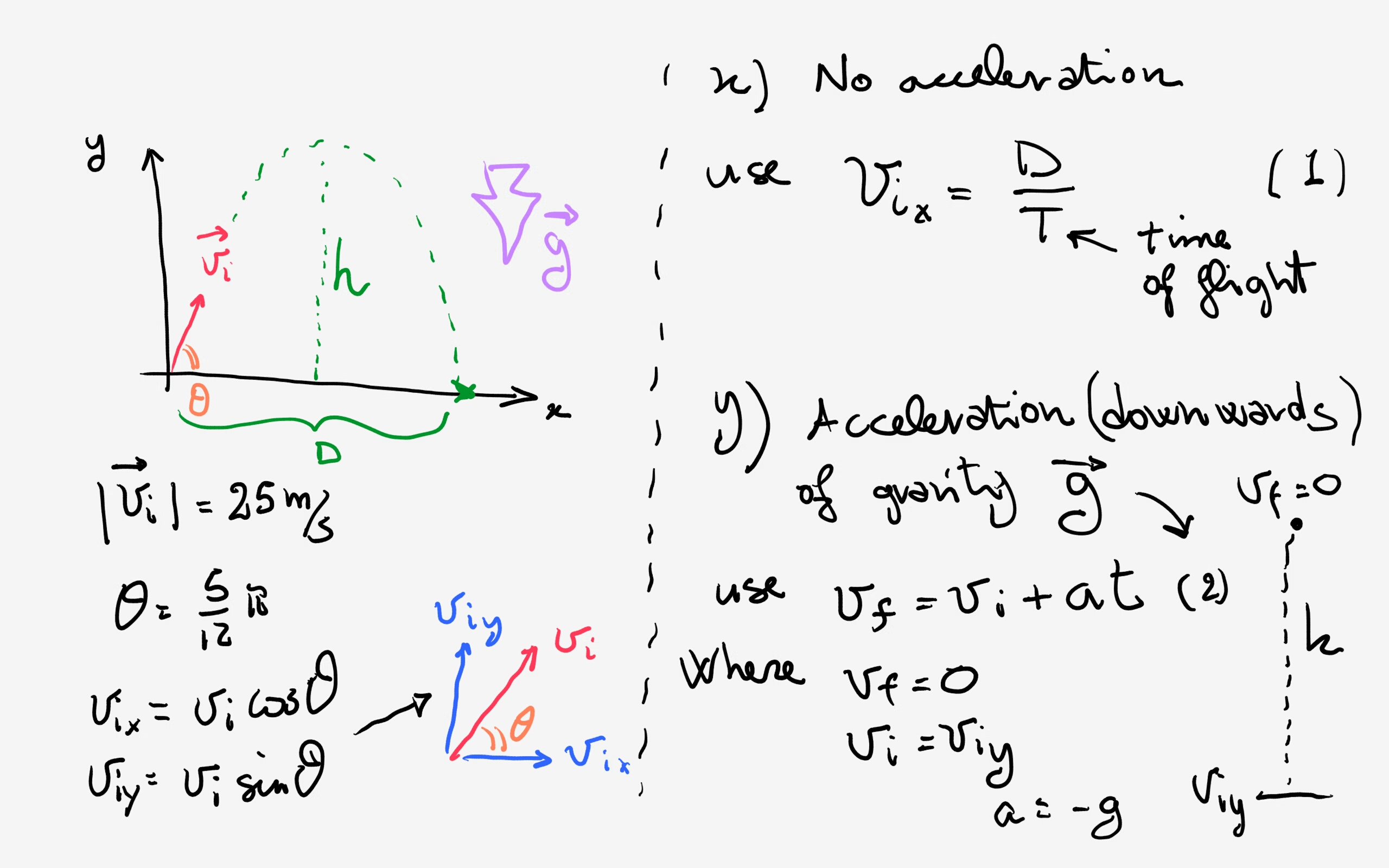
There were possible sources of error that were present in this lab. The main direction of solving a problem: try to derive equations that use these parameters.
#Projectile equations how to
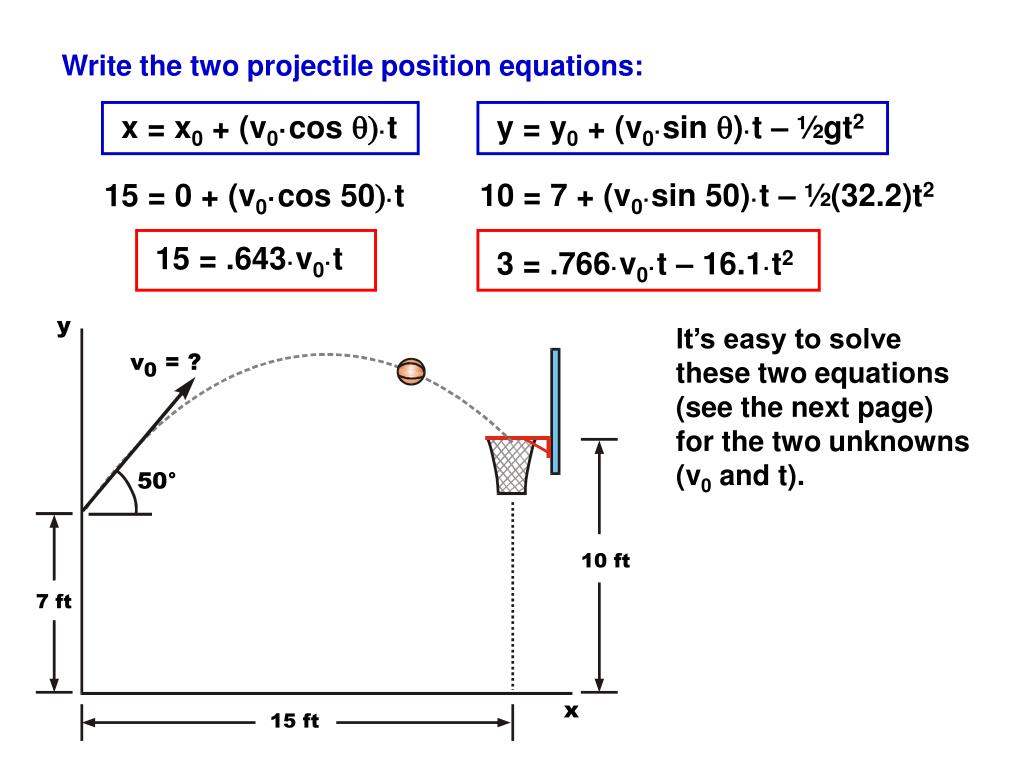
The predicted range was in close proximity with the average range the 0.018-meter difference between the two ranges resulted in a percent difference of 7.279%. General Physics :: Projectile Motion :: How to Calculate 1. By splitting the 0.033-meter difference between the highest range value and the lowest range value, I discovered that the range measurement uncertainty is 0.0165 meters. Include: horizontal and vertical components of motion of the. Throughout this lab, I have predicted the range of a projectile using a derived equation and certain variables, such as Vo, θ, and ΔY, in order to recognize how close my theory came to the average range found. Solve simple free-fall problems using the special equations for constant acceleration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
